NEET IMPORTANT INFORMATION AND DATES AT A GLANCE (Please refer to Information Bulletin for details)
The National Testing Agency (NTA) conducts National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET UG) in offline mode. The NEET UG is conducted once in a year. The single national-level undergraduate medical entrance exam, NEET UG will be held for admission to 645 medical, 318 dental, 914 AYUSH, and 47 BVSc and AH colleges in India.

Table of Contents
NEET Exam Impotant Date 2024
| NEET Online Application Start | 09 February 2024 |
| NEET Last Date of Application | 09 March 2024 (up to 05:00 PM) |
| Payment Last Date | 09 March 2024 (up to 11:50 PM) |
| Correction Date | coming soon |
| Official Website | Click Here |
| Bulletin | Click Here |
NEET New Syllabus 2024
Physics
Physics: Unit 01
| Physical world and measurement |
|---|
| Units of measurements, system of units, S.I. units, fundamental and derived units, least count, significant figures, errors in measurements, dimensions of physics quantities, dimensional analysis, and its applications |
Physics: Unit 02
| Kinematics |
|---|
| Frame of reference, motion in a straight line; position-time graph, speed, and velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion, average speed, and instantaneous velocity, uniformly accelerated motion, velocity-time, position-time graphs |
| Relation for uniformly accelerated motion, scalar and vector, vector |
| Addition and subtraction of vectors, scalar and vector products, unit vector |
| Resolution of a vector |
| Relative velocity, motion in a plane, projectile motion, uniform circular motion |
Physics: Unit 03
| Laws of motion |
|---|
| Force and inertia, Newton’s first law of motion; momentum, Newton’s second law of motion; impulse; Newton’s third law of motion |
| Law of conservation of linear momentum and its applications |
| Equilibrium of concurrent forces |
| Static and kinetic friction, laws of friction, rolling friction |
| Dynamics of uniform circular motion: Centripetal force and its applications, vehicle on level circular road, vehicle on banked road |
Physics: Unit 04
| Work, energy, and power |
|---|
| Work done by a constant force and variable force; kinetic energy and potential energies, work-energy theorem, power |
| The potential energy of a spring conservation of mechanical energy, conservative and non-conservative forces; motion in a vertical circle: Elastic and inelastic collisions in one and two dimensions |
Physics: Unit 05
| Rotational motion |
|---|
| Centre of mass of a two-particle system, centre of mass of a rigid body; basic concepts of rotational motion; moment of a force; torque, angular momentum, conservation of angular momentum and its applications; the moment of inertia, the radius of gyration |
| Values of moment of inertia for simple geometrical objects, parallel and perpendicular axes theorems, and their applications |
| Equilibrium of rigid bodies, rigid body rotation and equations of rotational motion, comparison of linear and rotational motions |
Physics: Unit 06
| Gravitation |
|---|
| The universal law of gravitation |
| Acceleration due to gravity and its variation with altitude and depth |
| Kepler’s laws of planetary motion |
| Gravitational potential energy; gravitational potential |
| Escape velocity, motion of a satellite, orbital velocity, time period and energy of satellite |
Physics: Unit 07
| Properties of solids and liquids |
|---|
| Elastic behaviour, stress-strain relationship, Hooke’s law |
| Young’s modulus, bulk modulus, modulus of rigidity |
| Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal’s law and its applications |
| Effect of gravity on fluid pressure |
| Viscosity |
| Stokes’ law |
| Terminal velocity, streamline and turbulent flow |
| Critical velocity |
| Bernoulli’s principle and its applications |
| Surface energy and surface tension, angle of contact, excess of pressure across of curved surface, application of surface tension-drops, bubbles and capillary rise |
| Heat, temperature, thermal expansion; specific heat capacity, calorimetry; change of state, latent heat |
| Heat transfer-conduction, convection, and radiation |
Physics: Unit 08
| Thermodynamics |
|---|
| Thermal equilibrium, zeroth law of thermodynamics, the concept of temperature |
| Heat, work, and internal energy |
| First law of thermodynamics, isothermal and adiabatic processes |
| Second law of the thermodynamics: Reversible and irreversible processes |
Physics: Unit 09
| Kinetic theory of gases |
|---|
| Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done on compressing a gas, kinetic theory of gases-assumptions, concept of pressure |
| Kinetic interpretation of temperature: RMS speed of gas molecules-degrees of freedom |
| Law of equipartition of energy and applications to specific heat capacities of gases; mean free path |
| Avogadro’s number |
Physics: Unit 10
| Oscillations and waves |
|---|
| Oscillations and periodic motion-time period, frequency, displacement as a function of time |
| Periodic functions |
| Simple Harmonic Motion (S.H.M.) and its equation; phase; oscillations of a spring-restoring force and force constant; energy in S.H.M.-kinetic and potential energies; simple pendulum-derivation of expression for its time period |
| Wave motion |
| Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of wave motion |
| Displacement relation for a progressive wave |
| Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves |
| Standing waves in strings and organ pipes, fundamental mode and harmonics |
| Beats |
Physics: Unit 11
| Electrostatics |
|---|
| Electric charges: conservation of charge |
| Coulomb’s law-force between two point charges, forces between multiple charges: Superposition principle and continuous charge distribution |
| Electric field: Electric field due to a point charge, electric field lines. Electric dipole, electric field due to a dipole. Torque on a dipole in a uniform electric field |
| Electric flux |
| Gauss’s law and its applications to find field due to infinitely long straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell |
| Electric potential and its calculation for a point charge, electric dipole and system of charges; potential difference, equipotential surfaces, electrical potential energy of a system of two point charges and of electric dipole in an electrostatic field |
| Conductors and insulators |
| Dielectrics and electric polarization, capacitors and capacitance, the combination of capacitors in series and in parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates |
| Energy stored in a capacitor |
Physics: Unit 12
| Current electricity |
|---|
| Electric current |
| Drift velocity, mobility, and their relation with electric current |
| Ohm’s law |
| Electrical resistance |
| V-I characteristics of Ohmic and non-Ohmic conductors |
| Electrical energy and power |
| Electrical resistivity, and conductivity |
| Series and parallel combinations of resistors; temperature dependence of resistance |
| Internal resistance of a cell, potential difference and EMF of a cell, a combination of cells in series and in parallel |
| Kirchhoff’s laws and simple applications |
| Wheatstone bridge |
| Meter bridge |
Physics: Unit 13
| Magnetic effects of current and magnetism |
|---|
| Biot-Savart law and its application to current carrying circular loop |
| Ampere’s law and its applications to infinitely long straight wire, straight and toroidal solenoids |
| Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields |
| Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field |
| Force between two parallel current-carrying conductors-definition of ampere |
| Torque experienced by a current loop in a magnetic field: Moving coil galvanometer-its current sensitivity and conversion to ammeter and voltmeter |
| Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment |
| Bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid; magnetic field line; magnetic field due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) arong its axis and perpendicular to its axis |
| Torque on a magnetic dipole in a uniform magnetic field |
| Para-, dia-, and ferro-magnetic substances with examples, effect of temperature on magnetic properties |
Physics: Unit 14
| Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents |
|---|
| Electromagnetic induction: Faraday’s law |
| Induced EMF and current; Lenz’s law, Eddy currents |
| Self and mutual inductance |
| Alternating currents, peak and RMS value of alternating current/ voltage: Reactance and impedance; LCR series circuit, resonance; power in AC circuits, wattless current |
| AC generator and transformer |
Physics: Unit 15
| Electromagnetic waves |
|---|
| Displacement current |
| Electromagnetic waves and their characteristics |
| Transverse nature of electromagnetic waves |
| Electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays), applications of E.M. waves |
Physics: Unit 16
| Optics |
|---|
| Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror formula |
| Refraction of light at plane and spherical surface, thin lens formula and lens maker formula |
| Total internal reflection and its applications |
| Magnification |
| Power of a lens |
| Combination of thin lenses in contact |
| Refraction of light through a prism |
| Microscope and astronomical telescope (reflecting and refracting ) and their magnifying powers |
| Wave optics: Wavefront and Huygens principle, laws of reflection and refraction using Huygens principle. Interference young’s double-slit experiment and expression for fringe width, coherent sources, and sustained interference of light |
| Wave optics: Diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maximum. Polarization, plane-polarized light: Brewster’s law, uses of plane-polarized light and polaroid |
Physics: Unit 17
| Dual nature of matter and radiation |
|---|
| Dual nature of radiation |
| Photoelectric effect |
| Hertz and Lenard’s observations; Einstein’s photoelectric equation: Particle nature of light |
| Matter waves-wave nature of particle, de Broglie relation |
Physics: Unit 18
| Atoms and nuclei |
|---|
| Alpha-particle scattering experiment; Rutherford’s model of atom; Bohr model, energy levels’ hydrogen spectrum |
| Composition and size of nucleus, atomic masses, mass-energy relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number, nuclear fission, and fusion |
Physics: Unit 19
| Electronic devices |
|---|
| Semiconductors; semiconductor diode: I-V characteristics in forward and reverse bias; diode as a rectifier; I-V characteristics of LED |
| The photodiode, solar cell, and Zener diode; Zener diode as a voltage regulator, logic gates (OR. AND. NOT. NAND and NOR) |
Physics: Unit 20
| Experimental skills |
|---|
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (1) Vernier calipers-its use to measure the internal and external diameter and depth of a vessel |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (2) Screw gauge-its use to determine thickness/ diameter of thin sheet/wire |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (3) Simple pendulum-dissipation of energy by plotting a graph between the square of amplitude and time |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (4) Metre scale-the mass of a given object by the principle of moments. (5) Young’s modulus of elasticity of the material of a metallic wire |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (6) Surface tension of water by capillary rise and effect of detergents |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (7) Coefficient of viscosity of a given viscous liquid by measuring terminal velocity of a given spherical body |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (8) Speed of sound in air at room temperature using a resonance tube. (9) Specific heat capacity of a given-(i) solid and (ii) liquid by method of mixtures |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (10) The resistivity of the material of a given wire using a metre bridge. (11) The resistance of a given wire using Ohm’s law |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (12) Resistance and figure of merit of a galvanometer by half deflection method |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (13) The focal length of; convex mirror, concave mirror, convex lens using the parallax method |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (14) The plot of the angle of deviation vs angle of incidence for a triangular prism |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (15) Refractive index of a glass slab using a travelling microscope. (16) Characteristic curves of a p-n junction diode in forward and reverse bias |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (17) Characteristic curves of a zener diode and finding reverse breakdown voltage |
| Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities: (18) Identification of diode. LED,. resistor. A capacitor from a mixed collection of such items |
Chemistry
Chemistry: Unit 01
| Some basic concepts in chemistry |
|---|
| Matter and its nature, Dalton’s atomic theory: Concept of atom, molecule, element. and compound: Laws of chemical combination; atomic and molecular masses, mole concept, molar mass, percentage composition |
| Empirical and molecular formulae: Chemical equations and stoichiometry |
Chemistry: Unit 02
| Atomic structure |
|---|
| Nature of electromagnetic radiation, photoelectric effect; spectrum of the hydrogen atom |
| Bohr model of a hydrogen atom-its postulates, derivation of the relations for the energy of the electron and radii of the different orbits, limitations of Bohr’s model; dual nature of matter, de Broglie’s relationship |
| Heisenberg uncertainty principle |
| Elementary ideas of quantum mechanics, quantum mechanics, the quantum mechanical model of the atom, its important features |
| Concept of atomic orbitals as one-electron wave functions: Variation of Ψ and Ψ2 with r for 1s and 2s orbitals; various quantum numbers (principal, angular momentum, arrd magnetic quantum numbers) and their significance |
| Shapes of s, p, and d – orbitals, electron spin and spin quantum number: Rules for filling electrons in orbitals-Aufbau principle |
| Pauli’s exclusion principle and Hund’s rule, electronic configuration of elements, extra stability of half-filled and completely filled orbitals |
Chemistry: Unit 03
| Chemical bonding and molecular structure |
|---|
| Kossel-Lewis approach to chemical bond formation, the concept of ionic and covalent bonds |
| Ionic bonding: Formation of ionic bonds, factors affecting the formation of ionic bonds; calculation of lattice enthalpy |
| Covalent bonding: Concept of electronegativity. Fajan’s rule, dipole moment: Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory and shapes of simple molecules |
| Quantum mechanical approach to covalent bonding: Valence bond theory-its important features, the concept of hybridization involving s, p, and d orbitals; resonance |
| Molecular orbital theory: Its important features. LCAOs, types of molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding), sigma and pi-bonds, molecular orbital electronic configuration of homonuclear diatomic molecules |
| Molecular orbital theory: The concept of bond order, bond length, and bond energy |
| Elementary idea of metallic bonding |
| Hydrogen bonding and is applications |
Chemistry: Unit 04
| Chemical thermodynamics |
|---|
| Fundamentals of thermodynamics: System and surroundings, extensive and intensive properties state functions, types of processes |
| The first law of thermodynamics: Concept of work, heat internal energy and enthalpy, heat capacity, molar heat capacity; Hess’s law of constant heat summation; enthalpies of bond dissociation, combustion formation, atomization, sublimation |
| The first law of thermodynamics: Phase transition, hydration, ionization and solution |
| The second law of thermodynamics: Spontaneity of processes; ∆S of the universe and ∆G of the system as criteria for spontaneity. ∆G◦ (standard Gibbs energy change) and equilibrium constant |
Chemistry: Unit 05
| Solutions |
|---|
| Different methods for expressing the concentration of solution-molarity, molarity, more fraction, percentage (by volume and mass both), the vapour pressure of solutions and Raoult’s law-Ideal and non-ideal solutions |
| Vapour pressure-composition, plots for ideal and non-ideal solutions; colligative properties of dilute solutions-a relative lowering of vapour pressure, depression or mass freezing point the elevation of boiling point and osmotic pressure |
| Determination of molecular mass; using colligative properties; abnormal value of molar mass, Van’t Hoff factor and its significance |
Chemistry: Unit 06
| Equilibrium |
|---|
| Meaning of equilibrium, the concept of dynamic equilibrium |
| Equilibria involving physical processes: Solid-liquid, liquid-gas and solid-gas equilibria, law, Henry’s law. General characteristics of equilibrium involving physical processes |
| Equilibrium involving physical processes: Law of chemical equilibrium, equilibrium constants (Kp and Kc) and their significance, the significance of ∆S and ∆G◦ in chemical equilibrium |
| Equilibrium involving physical processes: Factors affecting equilibrium concentration, pressure, temperature, catalyst; Le Chatelier’s principle |
| Ionic equilibrium: Weak and strong electrolytes, acids and bases (Arrhenius. Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis) and their ionization, Acid-base equilibria (Including multi stage ionization) and ionization constants, ionization of water |
| Ionic equilibrium: pH scale, common ion effect, hydrolysis of salts and pH of their solutions, the solubility of sparingly soluble salts and solubility products, buffer solutions |
Chemistry: Unit 07
| Redox reactions and electrochemistry |
|---|
| Electronic concepts of oxidation and reduction, redox reactions, oxidation number, rules for assigning oxidation reactions, oxidation number, balancing of redox reactions |
| Electrolytic and metallic conduction, conductance and their in electrolytic solutions, molar conductivities variation with concentration: Kohlrausch’s law and its applications |
| Electrochemical cells-electrolytic and galvanic cells, different potentials including types of electrodes, electrode potential including standard electrode potential, half cell and cell reaction |
| EMF of a galvanic cell and its measurement: Nernst equation and its applications; relationship between cell potential and gibbs energy change: Dry cell and lead accumulator; fuel cells |
Chemistry: Unit 08
| Chemical kinetics |
|---|
| Rate of a chemical reaction, factors affecting the rate of reactions: Concentration, temperature, pressure, and catalyst; elementary and complex reactions, order and molecularity of reactions, rate law, rate constant and its units |
| Differential and integral forms of zero and first-order reactions, their characteristics and half-lives, the effect of temperature on the rate of reactions, Arrhenius theory. activation energy and its calculation |
| Collision theory of bimolecular gaseous reactions (no derivation) |
Chemistry: Unit 09
| Classification of elements and periodicity in properties |
|---|
| Modern periodic law and present form of the periodic table. s, p. d and f block elements, periodic trends in properties of elements atomic and ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, valence, oxidation states, and chemical reactivity |
Chemistry: Unit 10
| P-block elements |
|---|
| Group-13 to group 18 elements: General introduction-electronic configuration and general trends in physical and chemical properties of elements across the periods and down the groups; unique behaviour of the first element in each group |
Chemistry: Unit 11
| d and f- block elements |
|---|
| Transition Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics, general trends in properties of the first-row transition elements – physical properties, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states |
| Transition Elements: Atomic radii. colour. catalytic behaviour. magnetic properties, complex formation, interstitial compounds, alloy formation; preparation, properties, and uses of K2Cr2O7, and KMnO4 |
| inner transition elements: Lanthanoids-electronic configuration, oxidation states, and lanthanoid contraction. Actinoids-electronic configuration and oxidation states |
Chemistry: Unit 12
| Coordination compounds |
|---|
| Introduction to coordination compounds |
| Werner’s theory; ligands, coordination number, denticity. Chelation; IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds, isomerism; bonding-valence bond approach and basic ideas of Crystal field theory, colour and magnetic properties |
| Importance of coordination compounds (in qualitative analysis, extraction of meals and in biological systems |
Chemistry: Unit 13
| Purification and characterisation of organic compounds |
|---|
| Purification: Crystallization, sublimation, distillation, differential extraction, and chromatography-principles and their applications |
| Qualitative analysis: Detection of nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus, and halogens |
| Quantitative analysis (basic principles only): Estimation of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, halogens, sulphur, phosphorus |
| Calculations of empirical formula and molecular formulae: Numerical problems in organic quantitative analysis |
Chemistry: Unit 14
| Some basic principles of organic chemistry |
|---|
| Tetravalency of carbon: Shapes of simple molecules-hybridization (s and p)-classification of organic compounds based on functional groups and those containing halogens, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur |
| Tetravalency of carbon: homologous series-Isomerism: Structural and stereoisomerism |
| Nomenclature (trivial and IUPAC): Covalent bond fission-homolytic and heterolytic: Free radicals, carbocations. and carbanions; stability of carbocations and free radicals, electrophiles, and nucleophiles |
| Electronic displacement in a covalent bond: Inductive effect, electromeric effect, resonance, and hyperconjugation |
| Common types of organic reactions: Substitution, addition, elimination, and rearrangement |
Chemistry: Unit 15
| Hydrocarbons |
|---|
| Classification, isomerism, IUPAC nomenclature, general methods of preparation, properties, and reactions |
| Alkanes: Conformations Sawhorse and Newman projections (of ethane) mechanism of halogenation of alkanes |
| Alkenes: Geometrical isomerism-mechanism of electrophilic addition: Addition of hydrogen, halogens, water, hydrogen halides (Markownikoff’s and peroxide effect) ozonolysis and polymerization |
| Alkynes: Acidic character-addition of hydrogen, water, and hydrogen halides; polymerization |
| Aromatic hydrocarbons: Nomenclature, benzene-structure and aromaticity: Mechanism of electrophilic substitution; halogenation, nitration |
| Friedel-crafts alkylation and acylation, directive influence of the functional group in mono- substituted benzene |
Chemistry: Unit 16
| Organic compounds containing halogens |
|---|
| General methods of preparation, properties, and reactions; nature of C-X bond; mechanisms of substitution reactions |
| Uses; environmental effects of chloroform, iodoform freons, and DDT |
Chemistry: Unit 17
| Organic compounds containing oxygen |
|---|
| General methods of preparation, properties, reactions, and uses |
| Alcohols, phenols & ethers: (i) Alcohols-identification of primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols; mechanism of dehydration. (ii) Phenols: Acidic nature, electrophilic substitution reactions, halogenation, nitration and sulphonation |
| Alcohols, phenols & ethers: (ii) Phenols-Reimer-Tiemann reaction. (iii) Ethers: Structure |
| Aldehyde and ketones: Nature of carbonyl group; nucleophilic addition to >c=o group, relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones; important reactions such as-nucleophilic addition reactions (addition of HCN. NH3, and its derivatives), Grignard reagent |
| Aldehyde and ketones: Oxidation reduction (Wolf Kishner and Clemmensen); the acidity of α-hydrogen. Aldol condensation, Cannizzaro reaction. Haloform reaction, chemical tests to distinguish between aldehydes and Ketones. Haloform reaction |
| Aldehyde and ketones: Chemical tests to distinguish between aldehydes and Ketones |
| Carboxylic acids |
| Acidic strength and factors affecting it |
Chemistry: Unit 18
| Organic compounds containing nitrogen |
|---|
| General methods of preparation. Properties, reactions, and uses |
| Amines: Nomenclature, classification structure, basic character, and identification of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines and their basic character |
| Diazonium salts: importance in synthetic organic chemistry |
Chemistry: Unit 19
| Biomolecules |
|---|
| General introduction and importance of biomolecules |
| Carbohydrates: Classification; aldoses and ketoses: Monosaccharides (glucose and fructose) and constituent monosaccharides of oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, and maltose) |
| Proteins: Elementary idea of α-amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides. Proteins: Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins, enzymes |
| Vitamins: Classification and functions |
| Nucleic acids: Chemical constitution of DNA and RNA |
| Biological functions of nucleic acids |
| Hormones (general introduction) |
Chemistry: Unit 20
| Principles related to practical, chemistry |
|---|
| Detection of extra elements (nitrogen, sulphur, halogens) in organic compounds; detection of the following functional group; hydroxyl (alcoholic and phenolic), carbonyl (aldehyde and ketones) carboxyl, and amino groups in organic compounds |
| The chemistry involved in the preparation of the following: (i) Inorganic compounds: Mohr’s salt, potash alum. (ii) Organic compounds: Acetanilide, p-nitro acetanilide, aniline yellow, iodoform |
| The chemistry involved in the titrimetric exercises: Acids, bases and the use of indicators, oxalic-acid vs KMnO4, Mohr’s salt vs KMnO4 |
| Chemical principles involved in the qualitative salt analysis: (i) Cations-Pb²⁺, Cu²⁺, Al³⁺, Fe³⁺, Zn²⁺, Ni²⁺, Ca²⁺, Ba²⁺, Mg²⁺, NH₄⁺. (b) Anions-CO²₃¯, S²¯, SO²₄¯, NO³¯, NO²¯, Cl¯, Br¯, I¯ (insoluble salts excluded) |
| Chemical principles involved in the following experiments: (i) Enthalpy of solution of CuSO4. (ii) Enthalpy of neutralization of strong acid and strong base. (iii) Preparation of lyophilic and lyophobic sols |
| Chemical principles involved in the following experiments: (iv) Kinetic study of the reaction of iodide ions with hydrogen peroxide at room temperature |
Zoology
Zoology: Unit 01
| Diversity in living world |
|---|
| Salient features and classification of animals-nonchordate up to phyla level and chordate up to classes level (three to five salient features and at least two examples) |
Zoology: Unit 02
| Structural organisation in animals and plants |
|---|
| Animal tissues; morphology, anatomy and functions of different systems (digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and reproductive) of an insect (frog). Brief account onlY |
Zoology: Unit 03
| Cell structure and function |
|---|
| Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life; structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell; plant cell and animal cell; cell envelope, cell membrane, cell wall; cell organelles-structure and function; endomembrane system-endoplasmic reticulum |
| Endomembrane system-golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles; mitochondria, ribosomes, plastids, micro bodies; cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, centrioles (ultra structure and function); nucleus-nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleolus |
| Chemical constituents of living cells: Biomolecules-structure and function of proteins, carbohydrates. lipids, nucleic acid; enzymes-types, properties, enzyme action, classification and nomenclature of enzymes |
| B cell division: Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and their significance |
Zoology: Unit 04
| Human physiology |
|---|
| Breathing and Respiration: Respiratory organs in animals (reca onry); respiratory system in humans; mechanism of breathing and its regulation in humans-exchange of gases, transport of gases and regulation of respiration respiratory volumes |
| Breathing and Respiration: Disorders related to respiration-asthma emphysema, occupational respiratory disorders |
| Body fluids and circulation: Composition of blood, blood groups, coagulation of brood; composition of lymph and its function; human circulatory system-structure of human heart and blood vessels; cardiac cycle, cardiac output, ECG, double circulation |
| Body fluids and circulation: Regulation of cardiac activity; disorders of circulatory system-hypertension, coronary artery disease, angina pectoris, heart failure |
| Excretory products and their elimination: Modes of excretion-ammonotelism, ureotelism, uricotelism; human excretory system-structure and function; urine formation, osmoregulation; regulation of kidney function-renin-angiotensin, atrial natriuretic factor |
| Excretory products and their elimination: Regulation of kidney function-ADH and diabetes insipidus; role of other organs in excretion; disorders; uraemia, renal failure, renal carcuri, nephritis; dialysis and artificial kidney |
| Locomotion and movement: Types of movement-ciliary, flagelar, muscular; skeletal muscle-contractile proteins and muscle contraction; skeletal system and its functions (To be dealt with the relevant practical of practical syllabus); Joints |
| Locomotion and movement: Disorders of muscular and skeletal system-myasthenia gravis, tetany, muscular dystrophy, arthritis, osteoporosis, gout |
| Neural control and coordination: Neuron and nerves; nervous system in humans, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system and visceral nervous system; generation and conduction of nerve impulse |
| Chemical coordination and regulation: Endocrine glands and hormones; human endocrine system-hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, gonads; mechanism of hormone action (elementary idea) |
| Chemical coordination and regulation: Role of hormones as messengers and regulators, hypo-and hyperactivity and related disorders (common disorders e.g. dwarfism, acromegaly, cretinism, goiter, exophthalmic goiter, diabetes, Addison’s disease) |
Zoology: Unit 05
| Reproduction |
|---|
| Human reproduction: Male and female reproductive systems; microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; gametogenesis- spermatogenesis & oogenesis; menstrual cycle; fertilisation, embryo development upto blastocyst formation, implantation |
| Human reproduction: Pregnancy and placenta formation (elementary idea); parturition (elementary idea); lactation (elementary idea) |
| Reproductive health: Need for reproductive health and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STD); birth control-need and methods, contraception and medical termination of pregnancy (MTP); amniocentesis |
| Reproductive health: Infertility and assisted reproductive technologies-IVF, ZIFT, GIFT (elementary idea for general awareness) |
Zoology: Unit 06
| Genetics and evolution |
|---|
| Heredity and variation: Chromosomes and genes; sex determination in humans, birds, honey bee; linkage and crossing over; sex linked inheritance-haemophilia colour blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans-thalassemia; chromosomal disorders in humans |
| Heredity and variation: Down’s syndrome, Turner’s and Klinefelter’s syndromes |
| Molecular basis of inheritance: Genome and human genome project; DNA fingerprinting, protein biosynthesis |
| Evolution: Origin of life; biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution from paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidence); Darwin’s contribution, modern synthetic theory of evolution |
| Evolution: Mechanism of evolution variation (mutation and recombination) and natural selection with examples, types of natural selection; gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy-Weinberg’s principle; adaptive radiation; human evolution |
Zoology: Unit 07
| Biology and human welfare |
|---|
| Health and Disease; pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (malaria, filariasis, ascariasis, typhoid, pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ringworm, dengue, chikungunya) |
| Basic concepts of immunology-vaccines; cancer, HIV and AIDS; adolescence, drug and alcohol abuse |
| Tobacco abuse |
| Microbes in human welfare: In household processing, industrial production, sewage treatment |
Zoology: Unit 08
| Biotechnology and its applications |
|---|
| Principles and process of biotechnology: Genetic engineering (recombinant DNA technology) |
| Application of biotechnology in health and agriculture: Human insulin and vaccine production, gene therapy genetically modified organisms-Bt crops; transgenic animals; biosafety issues-biopiracy and patents |
Botany
Botany: Unit 01
| Diversity in living world |
|---|
| What is living?; biodiversity; need for classification; taxonomy & systematics; concept of species and taxonomical hierarchy; binomial nomenclature |
| Five kingdom classification; salient features and classification of monera; protista and fungi into major groups; lichens; viruses and viroids |
| Salient features and classification of plants into major groups-algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms (three to five salient and distinguishing features and at least two examples of each category) |
Botany: Unit 02
| Structural organisation in animals and plants |
|---|
| Morphology and modifications; tissues; anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants: Root, stem, leaf, inflorescence-cymose and racemose |
| Anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants: Flower fruit and seed (to be dealt along with the relevant practical of the practical syllabus) family (malvaceae, cruciferae, leguminosae, compositae, gramineae) |
Botany: Unit 03
| Plant physiology |
|---|
| Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis as a means of autotrophic nutrition; site of photosynthesis take place; pigments involved in photosynthesis (elementary idea); photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis |
| Photosynthesis: Cyclic and non cyclic and photophosphorylation; chemiosmotic hypothesis; photorespiration C3 and C4 pathways; factors affecting photosynthesis |
| Respiration: Exchange gases; cellular respiration-glycolysis, fermentation (anaerobic), TCA cycle and electron transport system (aerobic); energy relations-number of ATP molecules generated; amphibolic pathways; respiratory quotient |
| Plant growth and development: Seed germination; phases of plant growth and plant growth rate; conditions of growth; differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation; sequence of developmental process in a plant cell; growth regulator-auxin |
| Plant growth and development: Growth regulator-gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene, ABA |
Botany: Unit 04
| Reproduction |
|---|
| Sexual reproduction in flowering plants: Flower structure; development of male and female gametophytes; pollination-types, agencies and examples; outbreeding devices; pollen-pistil interaction; double fertilization |
| Sexual reproduction in flowering plants: Post fertilization events-development of endosperm and embryo, development of seed and formation of fruit; special modes apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; significance of seed and fruit formation |
Botany: Unit 05
| Genetics and evolution |
|---|
| Heredity and variation: Mendelian inheritance; deviations from mendelism Incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles and inheritance of blood groups, pleiotropy; elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; chromosome theory of inheritance |
| Molecular basis of inheritance: Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; DNA replication; central dogma; transcription, genetic code, translation; gene expression and regulation-lac operon |
Botany: Unit 06
| Biology and human welfare |
|---|
| Microbes in human welfare: Energy generation and as biocontrol agents and biofertilizers |
Botany: Unit 07
| Ecology and environment |
|---|
| Organisms and environment: Population interactions-mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism, population attributes-growth, birth rate and death rate, age distribution |
| Ecosystem: Pattems, components; productivity and decomposition; energy flow; pyramids of number, biomass, energy |
| Biodiversity and its conservation: Concept of biodiversity; patterns of biodiversity; importance of biodiversity; loss of biodiversity; biodiversity conservation; hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction; red data book, biosphere reserves |
| Biodiversity and its conservation: National parks and sanctuaries, sacred groves |
Documents Required
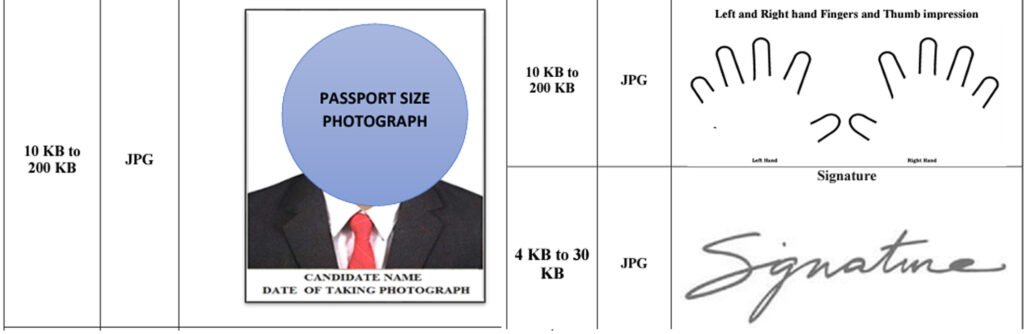
- Photo and Post Card Photo (4×6)
- Thumb
- HSLC Marksheet
- HS 1st Year Marksheet
- HS 2nd Year Marksheet (If Available)
- ID Proof (Aadhaar, PAN, Voter ID etc)
NEET Exam Previous Year Question Papers
Previous year’s NEET question paper all codes: (English & Hindi)
| NEET question combined sets | English | Hindi |
| E1+F1+G1+H1 | Click here | Click here |
| E2+F2+G2+H2 | Click here | Click here |
| E3+F3+G3+H3 | Click here | Click here |
| E4+F4+G4+H4 | Click here | Click here |
| E5+F5+G5+H5 | Click here | — |
| E6+F6+G6+H6 | Click here | — |
NEET exam papers: Regional languages
| NEET question paper language | Link |
| Telugu | Click here |
| Gujarati | Click here |
| Marathi | Click here |
| Tamil | Click here |
| Bengali | Click here |
| Kannada | Click here |
| Odia | Click here |
| Urdu | Click here |
| Assamese | Click here |
NEET application fee 2024
| Categories | Application fees |
| General | Rs. 1700/- |
| General-EWS/ OBC-NCL* | Rs 1600/- |
| SC/ST/PH/Third gender Candidates | Rs. 1000/- |
NEET Eligibility Criteria 2024
| Parameters | Eligibility criteria |
| Nationality | Indian Nationals, Foreign Nationals, NRI, PIO, OCI |
| Age requirement for NTA NEET 2024 | Born on or before 31-12-2007. Must have completed a minimum of 17 years of age at the time of admission as of 31 December 2024. |
| Minimum qualification | Candidates must have passed 10+2 with Physics, Chemistry, Biology/Biotechnology, and English as core subjects from a recognized board. |
| Minimum marks required in the qualifying examination | General – 50%, OBC/SC/ST – 40%, PWD – 40% |
| Number of permitted attempts |
Qualifications and Qualifying Examination Codes
- CODE: 01 – A candidate who is appearing in the qualifying examination, i.e., class 12 in 2024, whose result is awaited
- CODE: 02 – Candidates who have passed Class 12
- CODE: 03 – The Intermediate/Pre-degree Examination in Science of an Indian University/Board or other recognized
- CODE: 04 – The Pre-professional/Pre-medical Examination
- CODE: 05 – The first year of the three years’ degree course of a recognized University
- Full Details in Bulletin Click Here
Documents Required at Counselling
Documents List
- NEET 2024 admit card
- Rank letter/score card
- Date of birth certificate (if Class 10 pass certificate does not reflect the date of birth)
- Class 12 pass certificate
- Class 12 marks sheet
- Class 10 pass certificate
- Eight passport size photograph (same as affixed on NEET application form)
- Provisional allotment letter
- Identity proof
- Passport copy of sponsorer (only for NRI/OCI candidates)
- Sponsorship affidavit stating the sponsorer will take the responsibility for all the expenses incurred in the whole duration of the course (only for NRI/OCI candidates)
- Relationship affidavit stating the relationship of the candidate with the sponsorer (only for NRI/OCI candidates)
- Caste certificate (if applicable)
- Disability certificate (if applicable)
NEET Application Date (Year-wise Exam date vs Application date)
| Year | NEET exam date | NEET application release date |
| NEET 2024 | May 5, 2024 | February 9, 2024 |
| NEET 2023 | May 7, 2023 | March 6, 2023 |
| NEET 2022 | July 17, 2022 | April 6, 2022 |
| NEET 2021 | September 12, 2021 | July 13, 2021 |
| NEET 2020 | September 13, 2020 | December 2, 2019 |
| NEET 2019 | May 5, 2019 | November 1, 2018 |
NEET Applicant Statistics Over the Years
| Candidates | NEET 2023 | NEET 2022 | NEET 2021 | NEET 2020 | NEET 2019 | NEET 2018 | NEET 2017 |
| Number of candidates registered | 2087462 | 1872343 | 1614777 | 1597435 | 15,19,375 | 13,26,725 | 11,38,890 |
| Number of candidates appeared | 2038596 | 1764571 | 1544275 | 1366945 | 14,10,755 | 12,69,922 | 10,90,085 |
| Registered male candidates | 902936 | 807538 | 710979 | 716586 | 6,80,414 | 5,80,649 | 4,97,043 |
| Appeared male candidates | – | – | — | 618075 | 6,30,283 | 5,53,849 | 4,73,305 |
| Registered female candidates | 1184513 | 1064794 | 903782 | 880843 | 8,38,955 | 7,46,075 | 6,41,839 |
| Appeared female candidates | – | – | — | 748866 | 7,80,467 | 7,16,072 | 6,16,772 |
| Registered transgender candidates | 13 | 11 | 16 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 8 |